feat: add ragflow web project & add pnpm workspace file
This commit is contained in:
8
docs/guides/dataset/_category_.json
Normal file
8
docs/guides/dataset/_category_.json
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"label": "Datasets",
|
||||
"position": 0,
|
||||
"link": {
|
||||
"type": "generated-index",
|
||||
"description": "Guides on configuring a dataset."
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
72
docs/guides/dataset/autokeyword_autoquestion.mdx
Normal file
72
docs/guides/dataset/autokeyword_autoquestion.mdx
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: 3
|
||||
slug: /autokeyword_autoquestion
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Auto-keyword Auto-question
|
||||
import APITable from '@site/src/components/APITable';
|
||||
|
||||
Use a chat model to generate keywords or questions from each chunk in the dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
When selecting a chunking method, you can also enable auto-keyword or auto-question generation to increase retrieval rates. This feature uses a chat model to produce a specified number of keywords and questions from each created chunk, generating an "additional layer of information" from the original content.
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution WARNING
|
||||
Enabling this feature increases document indexing time and uses extra tokens, as all created chunks will be sent to the chat model for keyword or question generation.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## What is Auto-keyword?
|
||||
|
||||
Auto-keyword refers to the auto-keyword generation feature of RAGFlow. It uses a chat model to generate a set of keywords or synonyms from each chunk to correct errors and enhance retrieval accuracy. This feature is implemented as a slider under **Page rank** on the **Configuration** page of your dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
**Values**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 0: (Default) Disabled.
|
||||
- Between 3 and 5 (inclusive): Recommended if you have chunks of approximately 1,000 characters.
|
||||
- 30 (maximum)
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip NOTE
|
||||
- If your chunk size increases, you can increase the value accordingly. Please note, as the value increases, the marginal benefit decreases.
|
||||
- An Auto-keyword value must be an integer. If you set it to a non-integer, say 1.7, it will be rounded down to the nearest integer, which in this case is 1.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## What is Auto-question?
|
||||
|
||||
Auto-question is a feature of RAGFlow that automatically generates questions from chunks of data using a chat model. These questions (e.g. who, what, and why) also help correct errors and improve the matching of user queries. The feature usually works with FAQ retrieval scenarios involving product manuals or policy documents. And you can find this feature as a slider under **Page rank** on the **Configuration** page of your dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
**Values**:
|
||||
|
||||
- 0: (Default) Disabled.
|
||||
- 1 or 2: Recommended if you have chunks of approximately 1,000 characters.
|
||||
- 10 (maximum)
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip NOTE
|
||||
- If your chunk size increases, you can increase the value accordingly. Please note, as the value increases, the marginal benefit decreases.
|
||||
- An Auto-question value must be an integer. If you set it to a non-integer, say 1.7, it will be rounded down to the nearest integer, which in this case is 1.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Tips from the community
|
||||
|
||||
The Auto-keyword or Auto-question values relate closely to the chunking size in your dataset. However, if you are new to this feature and unsure which value(s) to start with, the following are some value settings we gathered from our community. While they may not be accurate, they provide a starting point at the very least.
|
||||
|
||||
```mdx-code-block
|
||||
<APITable>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| Use cases or typical scenarios | Document volume/length | Auto_keyword (0–30) | Auto_question (0–10) |
|
||||
|---------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------|----------------------------|----------------------------|
|
||||
| Internal process guidance for employee handbook | Small, under 10 pages | 0 | 0 |
|
||||
| Customer service FAQs | Medium, 10–100 pages | 3–7 | 1–3 |
|
||||
| Technical whitepapers: Development standards, protocol details | Large, over 100 pages | 2–4 | 1–2 |
|
||||
| Contracts / Regulations / Legal clause retrieval | Large, over 50 pages | 2–5 | 0–1 |
|
||||
| Multi-repository layered new documents + old archive | Many | Adjust as appropriate |Adjust as appropriate |
|
||||
| Social media comment pool: multilingual & mixed spelling | Very large volume of short text | 8–12 | 0 |
|
||||
| Operational logs for troubleshooting | Very large volume of short text | 3–6 | 0 |
|
||||
| Marketing asset library: multilingual product descriptions | Medium | 6–10 | 1–2 |
|
||||
| Training courses / eBooks | Large | 2–5 | 1–2 |
|
||||
| Maintenance manual: equipment diagrams + steps | Medium | 3–7 | 1–2 |
|
||||
|
||||
```mdx-code-block
|
||||
</APITable>
|
||||
```
|
||||
8
docs/guides/dataset/best_practices/_category_.json
Normal file
8
docs/guides/dataset/best_practices/_category_.json
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,8 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"label": "Best practices",
|
||||
"position": 11,
|
||||
"link": {
|
||||
"type": "generated-index",
|
||||
"description": "Best practices on configuring a dataset."
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: 1
|
||||
slug: /accelerate_doc_indexing
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Accelerate indexing
|
||||
import APITable from '@site/src/components/APITable';
|
||||
|
||||
A checklist to speed up document parsing and indexing.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that some of your settings may consume a significant amount of time. If you often find that document parsing is time-consuming, here is a checklist to consider:
|
||||
|
||||
- Use GPU to reduce embedding time.
|
||||
- On the configuration page of your dataset, switch off **Use RAPTOR to enhance retrieval**.
|
||||
- Extracting knowledge graph (GraphRAG) is time-consuming.
|
||||
- Disable **Auto-keyword** and **Auto-question** on the configuration page of your dataset, as both depend on the LLM.
|
||||
- **v0.17.0+:** If all PDFs in your dataset are plain text and do not require GPU-intensive processes like OCR (Optical Character Recognition), TSR (Table Structure Recognition), or DLA (Document Layout Analysis), you can choose **Naive** over **DeepDoc** or other time-consuming large model options in the **Document parser** dropdown. This will substantially reduce document parsing time.
|
||||
152
docs/guides/dataset/configure_knowledge_base.md
Normal file
152
docs/guides/dataset/configure_knowledge_base.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: -10
|
||||
slug: /configure_knowledge_base
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Configure dataset
|
||||
|
||||
Most of RAGFlow's chat assistants and Agents are based on datasets. Each of RAGFlow's datasets serves as a knowledge source, *parsing* files uploaded from your local machine and file references generated in **File Management** into the real 'knowledge' for future AI chats. This guide demonstrates some basic usages of the dataset feature, covering the following topics:
|
||||
|
||||
- Create a dataset
|
||||
- Configure a dataset
|
||||
- Search for a dataset
|
||||
- Delete a dataset
|
||||
|
||||
## Create dataset
|
||||
|
||||
With multiple datasets, you can build more flexible, diversified question answering. To create your first dataset:
|
||||
|
||||
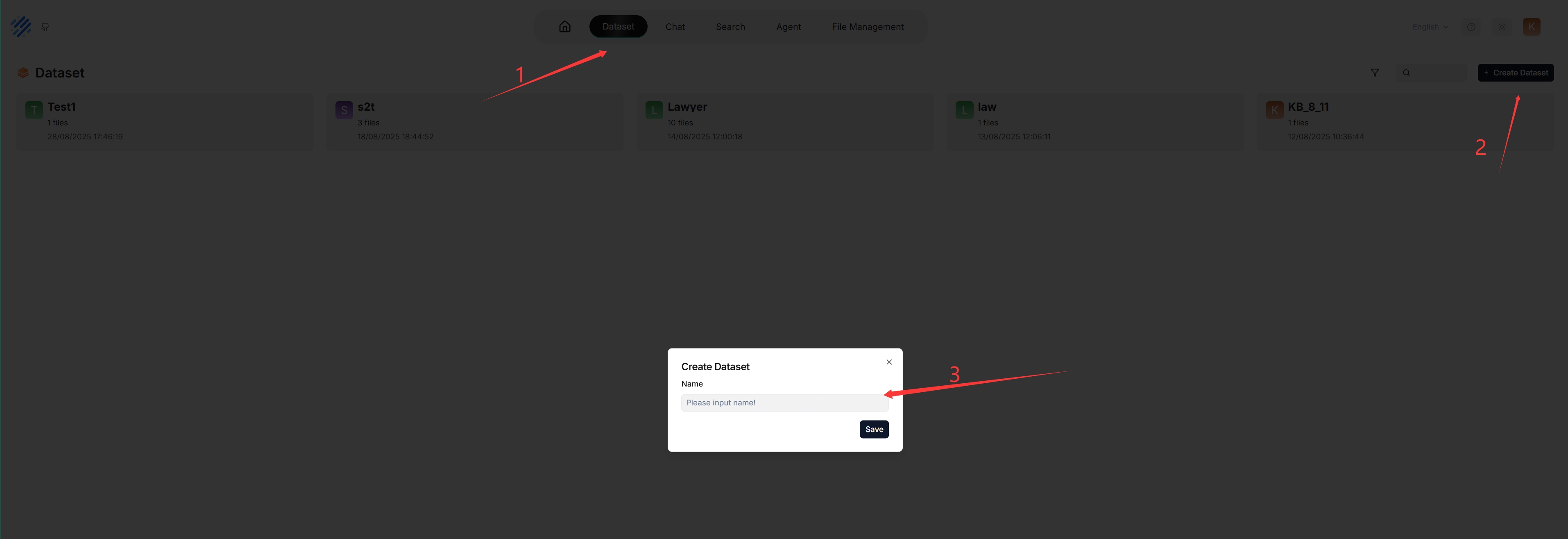
|
||||
|
||||
_Each time a dataset is created, a folder with the same name is generated in the **root/.knowledgebase** directory._
|
||||
|
||||
## Configure dataset
|
||||
|
||||
The following screenshot shows the configuration page of a dataset. A proper configuration of your dataset is crucial for future AI chats. For example, choosing the wrong embedding model or chunking method would cause unexpected semantic loss or mismatched answers in chats.
|
||||
|
||||
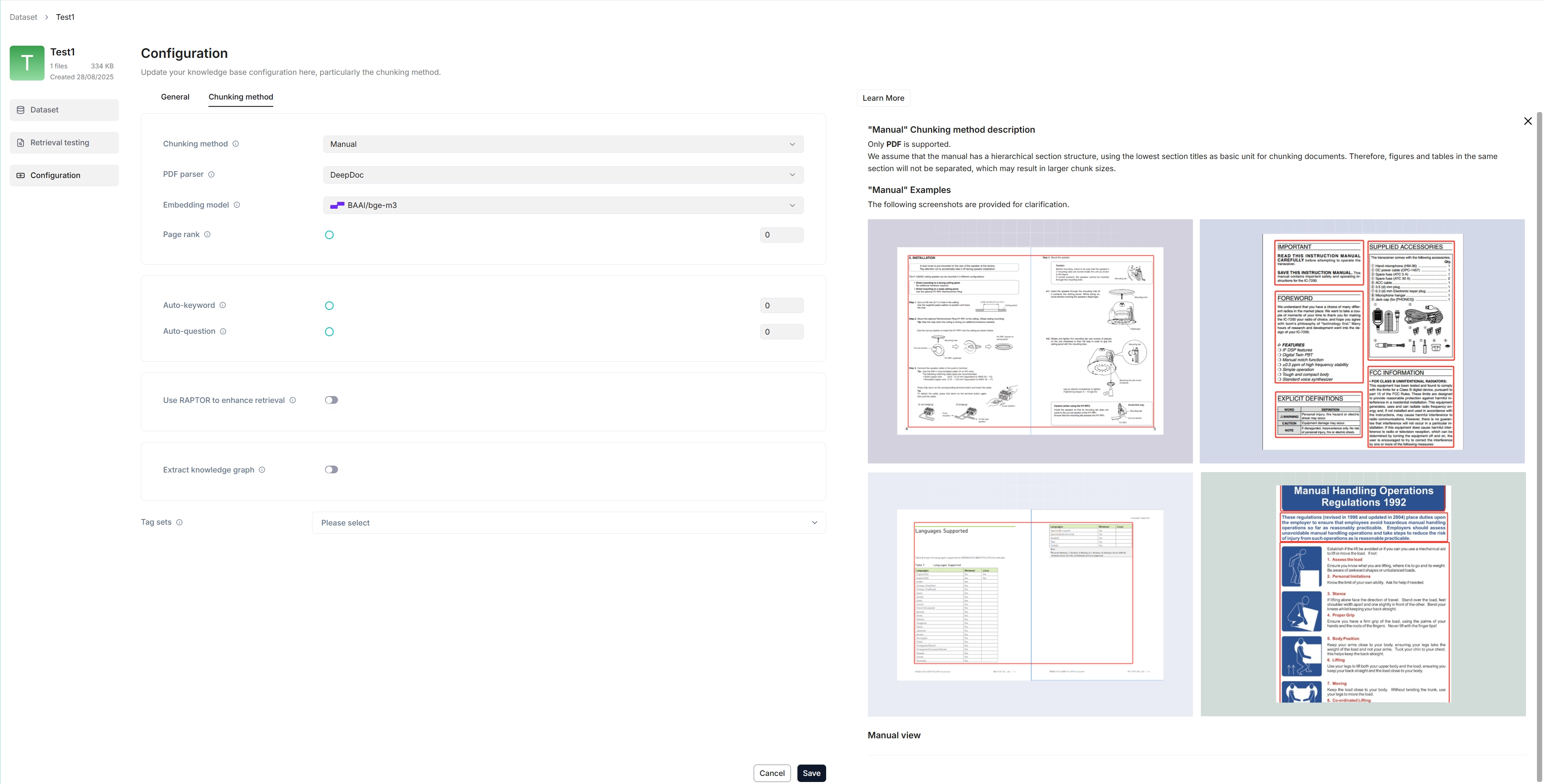
|
||||
|
||||
This section covers the following topics:
|
||||
|
||||
- Select chunking method
|
||||
- Select embedding model
|
||||
- Upload file
|
||||
- Parse file
|
||||
- Intervene with file parsing results
|
||||
- Run retrieval testing
|
||||
|
||||
### Select chunking method
|
||||
|
||||
RAGFlow offers multiple built-in chunking template to facilitate chunking files of different layouts and ensure semantic integrity. From the **Built-in** chunking method dropdown under **Parse type**, you can choose the default template that suits the layouts and formats of your files. The following table shows the descriptions and the compatible file formats of each supported chunk template:
|
||||
|
||||
| **Template** | Description | File format |
|
||||
|--------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| General | Files are consecutively chunked based on a preset chunk token number. | MD, MDX, DOCX, XLSX, XLS (Excel 97-2003), PPT, PDF, TXT, JPEG, JPG, PNG, TIF, GIF, CSV, JSON, EML, HTML |
|
||||
| Q&A | | XLSX, XLS (Excel 97-2003), CSV/TXT |
|
||||
| Resume | Enterprise edition only. You can also try it out on demo.ragflow.io. | DOCX, PDF, TXT |
|
||||
| Manual | | PDF |
|
||||
| Table | | XLSX, XLS (Excel 97-2003), CSV/TXT |
|
||||
| Paper | | PDF |
|
||||
| Book | | DOCX, PDF, TXT |
|
||||
| Laws | | DOCX, PDF, TXT |
|
||||
| Presentation | | PDF, PPTX |
|
||||
| Picture | | JPEG, JPG, PNG, TIF, GIF |
|
||||
| One | Each document is chunked in its entirety (as one). | DOCX, XLSX, XLS (Excel 97-2003), PDF, TXT |
|
||||
| Tag | The dataset functions as a tag set for the others. | XLSX, CSV/TXT |
|
||||
|
||||
You can also change a file's chunking method on the **Files** page.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>From v0.21.1 onward, RAGFlow supports ingestion pipeline for customized data ingestion and cleansing workflows.</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
To use a customized data pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
1. On the **Agent** page, click **+ Create agent** > **Create from blank**.
|
||||
2. Select **Ingestion pipeline** and name your data pipeline in the popup, then click **Save** to show the data pipeline canvas.
|
||||
3. After updating your data pipeline, click **Save** on the top right of the canvas.
|
||||
4. Navigate to the **Configuration** page of your dataset, select **Choose pipeline** in **Ingestion pipeline**.
|
||||
|
||||
*Your saved data pipeline will appear in the dropdown menu below.*
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### Select embedding model
|
||||
|
||||
An embedding model converts chunks into embeddings. It cannot be changed once the dataset has chunks. To switch to a different embedding model, you must delete all existing chunks in the dataset. The obvious reason is that we *must* ensure that files in a specific dataset are converted to embeddings using the *same* embedding model (ensure that they are compared in the same embedding space).
|
||||
|
||||
The following embedding models can be deployed locally:
|
||||
|
||||
- BAAI/bge-large-zh-v1.5
|
||||
- maidalun1020/bce-embedding-base_v1
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger IMPORTANT
|
||||
These two embedding models are optimized specifically for English and Chinese, so performance may be compromised if you use them to embed documents in other languages.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Upload file
|
||||
|
||||
- RAGFlow's **File Management** allows you to link a file to multiple datasets, in which case each target dataset holds a reference to the file.
|
||||
- In **Knowledge Base**, you are also given the option of uploading a single file or a folder of files (bulk upload) from your local machine to a dataset, in which case the dataset holds file copies.
|
||||
|
||||
While uploading files directly to a dataset seems more convenient, we *highly* recommend uploading files to **File Management** and then linking them to the target datasets. This way, you can avoid permanently deleting files uploaded to the dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
### Parse file
|
||||
|
||||
File parsing is a crucial topic in dataset configuration. The meaning of file parsing in RAGFlow is twofold: chunking files based on file layout and building embedding and full-text (keyword) indexes on these chunks. After having selected the chunking method and embedding model, you can start parsing a file:
|
||||
|
||||
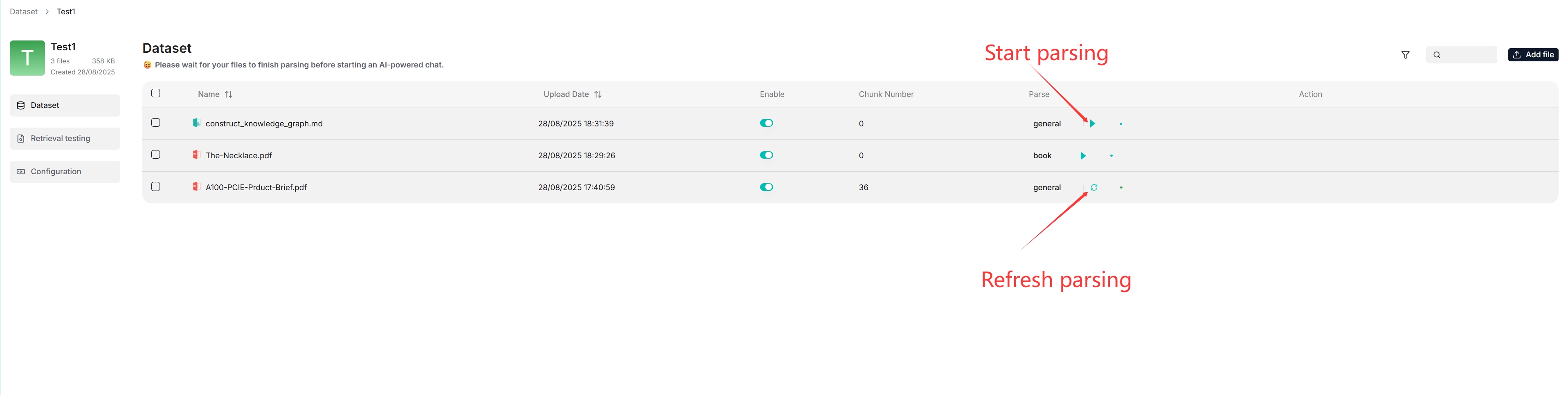
|
||||
|
||||
- As shown above, RAGFlow allows you to use a different chunking method for a particular file, offering flexibility beyond the default method.
|
||||
- As shown above, RAGFlow allows you to enable or disable individual files, offering finer control over dataset-based AI chats.
|
||||
|
||||
### Intervene with file parsing results
|
||||
|
||||
RAGFlow features visibility and explainability, allowing you to view the chunking results and intervene where necessary. To do so:
|
||||
|
||||
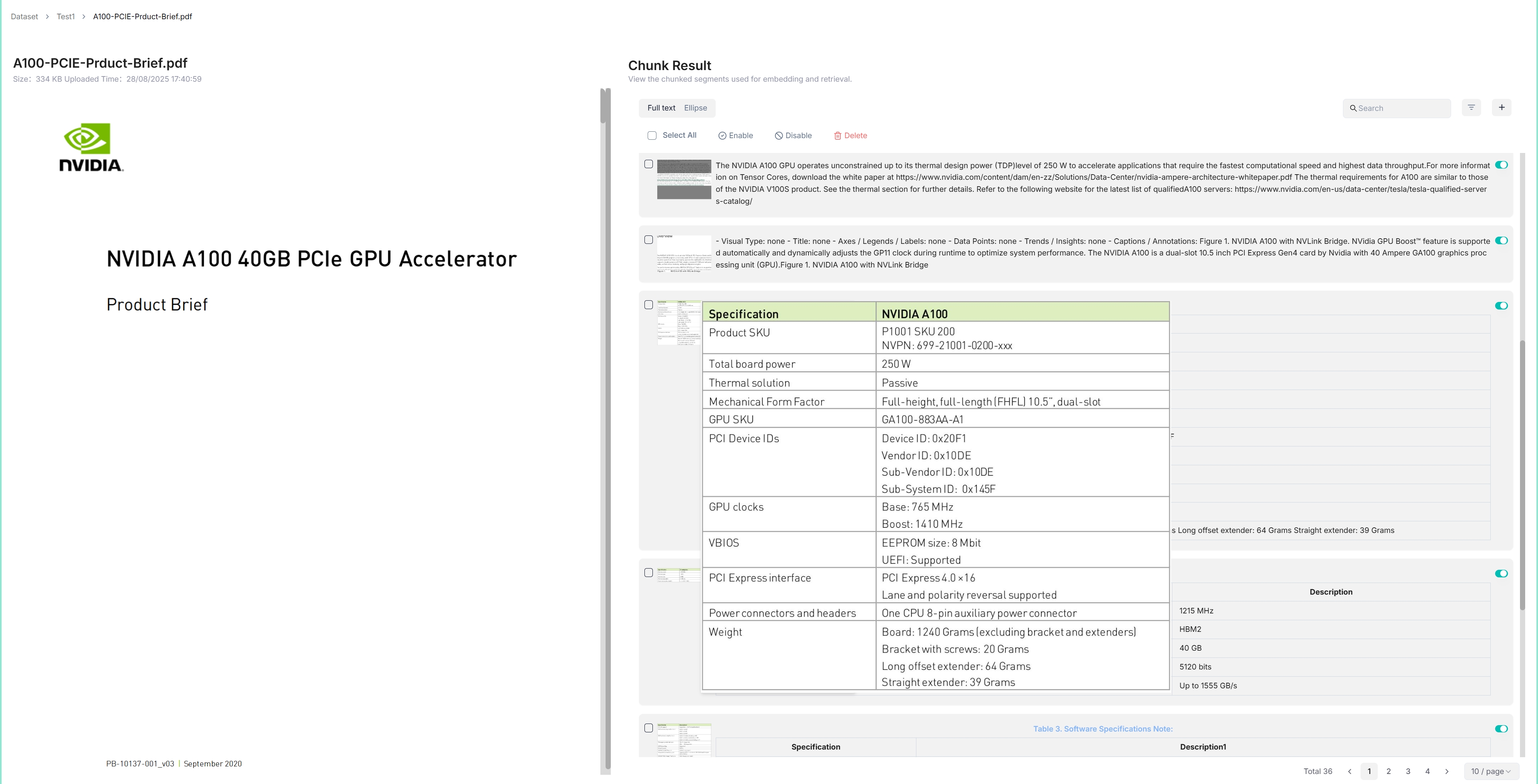
1. Click on the file that completes file parsing to view the chunking results:
|
||||
|
||||
_You are taken to the **Chunk** page:_
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. Hover over each snapshot for a quick view of each chunk.
|
||||
|
||||
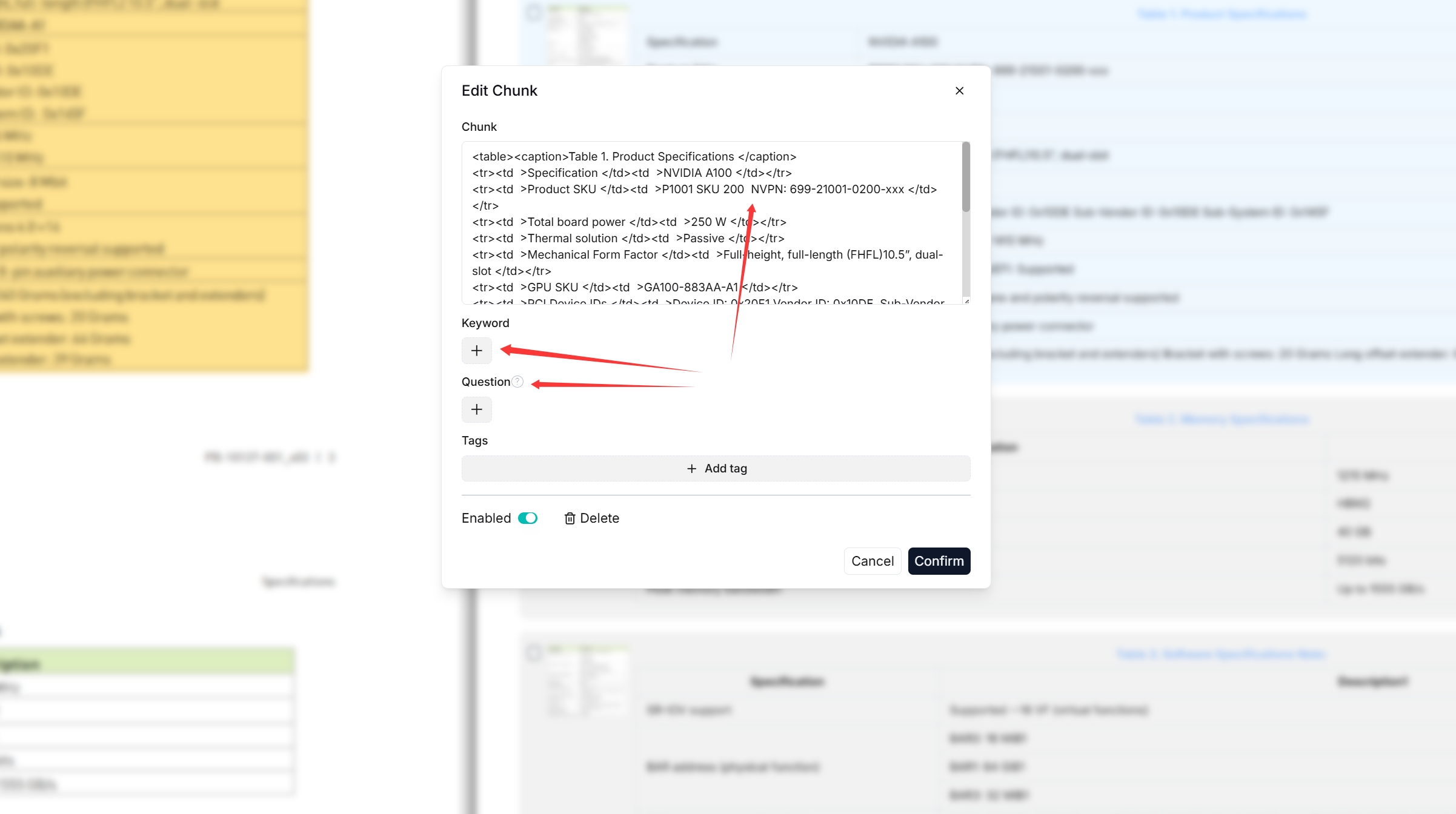
3. Double-click the chunked texts to add keywords, questions, tags, or make *manual* changes where necessary:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution NOTE
|
||||
You can add keywords to a file chunk to increase its ranking for queries containing those keywords. This action increases its keyword weight and can improve its position in search list.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
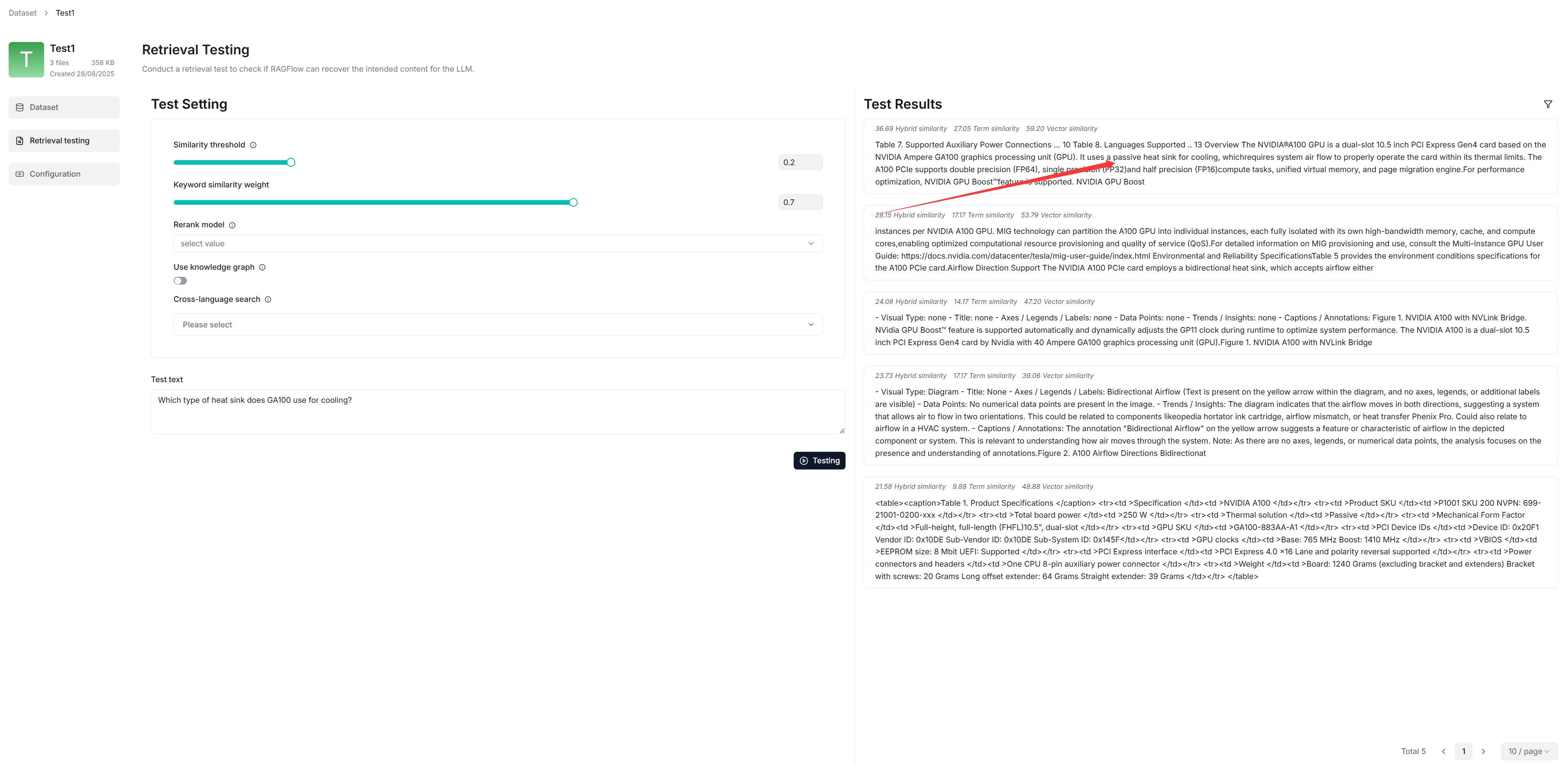
4. In Retrieval testing, ask a quick question in **Test text** to double-check if your configurations work:
|
||||
|
||||
_As you can tell from the following, RAGFlow responds with truthful citations._
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Run retrieval testing
|
||||
|
||||
RAGFlow uses multiple recall of both full-text search and vector search in its chats. Prior to setting up an AI chat, consider adjusting the following parameters to ensure that the intended information always turns up in answers:
|
||||
|
||||
- Similarity threshold: Chunks with similarities below the threshold will be filtered. By default, it is set to 0.2.
|
||||
- Vector similarity weight: The percentage by which vector similarity contributes to the overall score. By default, it is set to 0.3.
|
||||
|
||||
See [Run retrieval test](./run_retrieval_test.md) for details.
|
||||
|
||||
## Search for dataset
|
||||
|
||||
As of RAGFlow v0.21.1, the search feature is still in a rudimentary form, supporting only dataset search by name.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Delete dataset
|
||||
|
||||
You are allowed to delete a dataset. Hover your mouse over the three dot of the intended dataset card and the **Delete** option appears. Once you delete a dataset, the associated folder under **root/.knowledge** directory is AUTOMATICALLY REMOVED. The consequence is:
|
||||
|
||||
- The files uploaded directly to the dataset are gone;
|
||||
- The file references, which you created from within **File Management**, are gone, but the associated files still exist in **File Management**.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
102
docs/guides/dataset/construct_knowledge_graph.md
Normal file
102
docs/guides/dataset/construct_knowledge_graph.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: 8
|
||||
slug: /construct_knowledge_graph
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Construct knowledge graph
|
||||
|
||||
Generate a knowledge graph for your dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
To enhance multi-hop question-answering, RAGFlow adds a knowledge graph construction step between data extraction and indexing, as illustrated below. This step creates additional chunks from existing ones generated by your specified chunking method.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
From v0.16.0 onward, RAGFlow supports constructing a knowledge graph on a dataset, allowing you to construct a *unified* graph across multiple files within your dataset. When a newly uploaded file starts parsing, the generated graph will automatically update.
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger WARNING
|
||||
Constructing a knowledge graph requires significant memory, computational resources, and tokens.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Scenarios
|
||||
|
||||
Knowledge graphs are especially useful for multi-hop question-answering involving *nested* logic. They outperform traditional extraction approaches when you are performing question answering on books or works with complex entities and relationships.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip NOTE
|
||||
RAPTOR (Recursive Abstractive Processing for Tree Organized Retrieval) can also be used for multi-hop question-answering tasks. See [Enable RAPTOR](./enable_raptor.md) for details. You may use either approach or both, but ensure you understand the memory, computational, and token costs involved.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
The system's default chat model is used to generate knowledge graph. Before proceeding, ensure that you have a chat model properly configured:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Configurations
|
||||
|
||||
### Entity types (*Required*)
|
||||
|
||||
The types of the entities to extract from your dataset. The default types are: **organization**, **person**, **event**, and **category**. Add or remove types to suit your specific dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
### Method
|
||||
|
||||
The method to use to construct knowledge graph:
|
||||
|
||||
- **General**: Use prompts provided by [GraphRAG](https://github.com/microsoft/graphrag) to extract entities and relationships.
|
||||
- **Light**: (Default) Use prompts provided by [LightRAG](https://github.com/HKUDS/LightRAG) to extract entities and relationships. This option consumes fewer tokens, less memory, and fewer computational resources.
|
||||
|
||||
### Entity resolution
|
||||
|
||||
Whether to enable entity resolution. You can think of this as an entity deduplication switch. When enabled, the LLM will combine similar entities - e.g., '2025' and 'the year of 2025', or 'IT' and 'Information Technology' - to construct a more effective graph.
|
||||
|
||||
- (Default) Disable entity resolution.
|
||||
- Enable entity resolution. This option consumes more tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
### Community reports
|
||||
|
||||
In a knowledge graph, a community is a cluster of entities linked by relationships. You can have the LLM generate an abstract for each community, known as a community report. See [here](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/graphrag-improving-global-search-via-dynamic-community-selection/) for more information. This indicates whether to generate community reports:
|
||||
|
||||
- Generate community reports. This option consumes more tokens.
|
||||
- (Default) Do not generate community reports.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to the **Configuration** page of your dataset and update:
|
||||
|
||||
- Entity types: *Required* - Specifies the entity types in the knowledge graph to generate. You don't have to stick with the default, but you need to customize them for your documents.
|
||||
- Method: *Optional*
|
||||
- Entity resolution: *Optional*
|
||||
- Community reports: *Optional*
|
||||
*The default knowledge graph configurations for your dataset are now set.*
|
||||
|
||||
2. Navigate to the **Files** page of your dataset, click the **Generate** button on the top right corner of the page, then select **Knowledge graph** from the dropdown to initiate the knowledge graph generation process.
|
||||
|
||||
*You can click the pause button in the dropdown to halt the build process when necessary.*
|
||||
|
||||
3. Go back to the **Configuration** page:
|
||||
|
||||
*Once a knowledge graph is generated, the **Knowledge graph** field changes from `Not generated` to `Generated at a specific timestamp`. You can delete it by clicking the recycle bin button to the right of the field.*
|
||||
|
||||
4. To use the created knowledge graph, do either of the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- In the **Chat setting** panel of your chat app, switch on the **Use knowledge graph** toggle.
|
||||
- If you are using an agent, click the **Retrieval** agent component to specify the dataset(s) and switch on the **Use knowledge graph** toggle.
|
||||
|
||||
## Frequently asked questions
|
||||
|
||||
### Does the knowledge graph automatically update when I remove a related file?
|
||||
|
||||
Nope. The knowledge graph does *not* update *until* you regenerate a knowledge graph for your dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to remove a generated knowledge graph?
|
||||
|
||||
On the **Configuration** page of your dataset, find the **Knoweledge graph** field and click the recycle bin button to the right of the field.
|
||||
|
||||
### Where is the created knowledge graph stored?
|
||||
|
||||
All chunks of the created knowledge graph are stored in RAGFlow's document engine: either Elasticsearch or [Infinity](https://github.com/infiniflow/infinity).
|
||||
|
||||
### How to export a created knowledge graph?
|
||||
|
||||
Nope. Exporting a created knowledge graph is not supported. If you still consider this feature essential, please [raise an issue](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/issues) explaining your use case and its importance.
|
||||
42
docs/guides/dataset/enable_excel2html.md
Normal file
42
docs/guides/dataset/enable_excel2html.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
slug: /enable_excel2html
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable Excel2HTML
|
||||
|
||||
Convert complex Excel spreadsheets into HTML tables.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
When using the **General** chunking method, you can enable the **Excel to HTML** toggle to convert spreadsheet files into HTML tables. If it is disabled, spreadsheet tables will be represented as key-value pairs. For complex tables that cannot be simply represented this way, you must enable this feature.
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution WARNING
|
||||
The feature is disabled by default. If your dataset contains spreadsheets with complex tables and you do not enable this feature, RAGFlow will not throw an error but your tables are likely to be garbled.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Scenarios
|
||||
|
||||
Works with complex tables that cannot be represented as key-value pairs. Examples include spreadsheet tables with multiple columns, tables with merged cells, or multiple tables within one sheet. In such cases, consider converting these spreadsheet tables into HTML tables.
|
||||
|
||||
## Considerations
|
||||
|
||||
- The Excel2HTML feature applies only to spreadsheet files (XLSX or XLS (Excel 97-2003)).
|
||||
- This feature is associated with the **General** chunking method. In other words, it is available *only when* you select the **General** chunking method.
|
||||
- When this feature is enabled, spreadsheet tables with more than 12 rows will be split into chunks of 12 rows each.
|
||||
|
||||
## Procedure
|
||||
|
||||
1. On your dataset's **Configuration** page, select **General** as the chunking method.
|
||||
|
||||
_The **Excel to HTML** toggle appears._
|
||||
|
||||
2. Enable **Excel to HTML** if your dataset contains complex spreadsheet tables that cannot be represented as key-value pairs.
|
||||
3. Leave **Excel to HTML** disabled if your dataset has no spreadsheet tables or if its spreadsheet tables can be represented as key-value pairs.
|
||||
4. If question-answering regarding complex tables is unsatisfactory, check if **Excel to HTML** is enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
## Frequently asked questions
|
||||
|
||||
### Should I enable this feature for PDFs with complex tables?
|
||||
|
||||
Nope. This feature applies to spreadsheet files only. Enabling **Excel to HTML** does not affect your PDFs.
|
||||
93
docs/guides/dataset/enable_raptor.md
Normal file
93
docs/guides/dataset/enable_raptor.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: 7
|
||||
slug: /enable_raptor
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable RAPTOR
|
||||
|
||||
A recursive abstractive method used in long-context knowledge retrieval and summarization, balancing broad semantic understanding with fine details.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
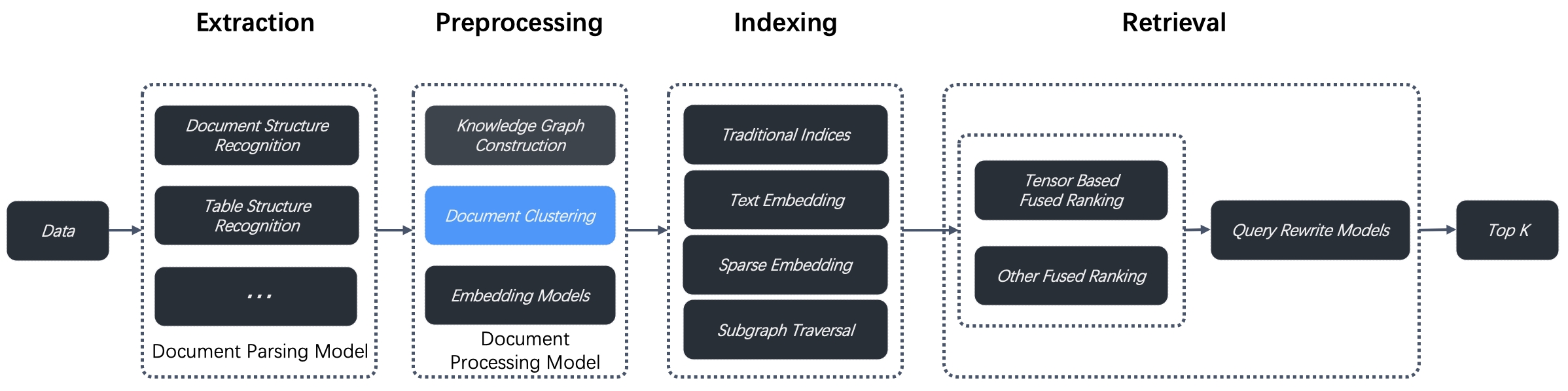
RAPTOR (Recursive Abstractive Processing for Tree Organized Retrieval) is an enhanced document preprocessing technique introduced in a [2024 paper](https://arxiv.org/html/2401.18059v1). Designed to tackle multi-hop question-answering issues, RAPTOR performs recursive clustering and summarization of document chunks to build a hierarchical tree structure. This enables more context-aware retrieval across lengthy documents. RAGFlow v0.6.0 integrates RAPTOR for document clustering as part of its data preprocessing pipeline between data extraction and indexing, as illustrated below.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Our tests with this new approach demonstrate state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on question-answering tasks requiring complex, multi-step reasoning. By combining RAPTOR retrieval with our built-in chunking methods and/or other retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) approaches, you can further improve your question-answering accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger WARNING
|
||||
Enabling RAPTOR requires significant memory, computational resources, and tokens.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Basic principles
|
||||
|
||||
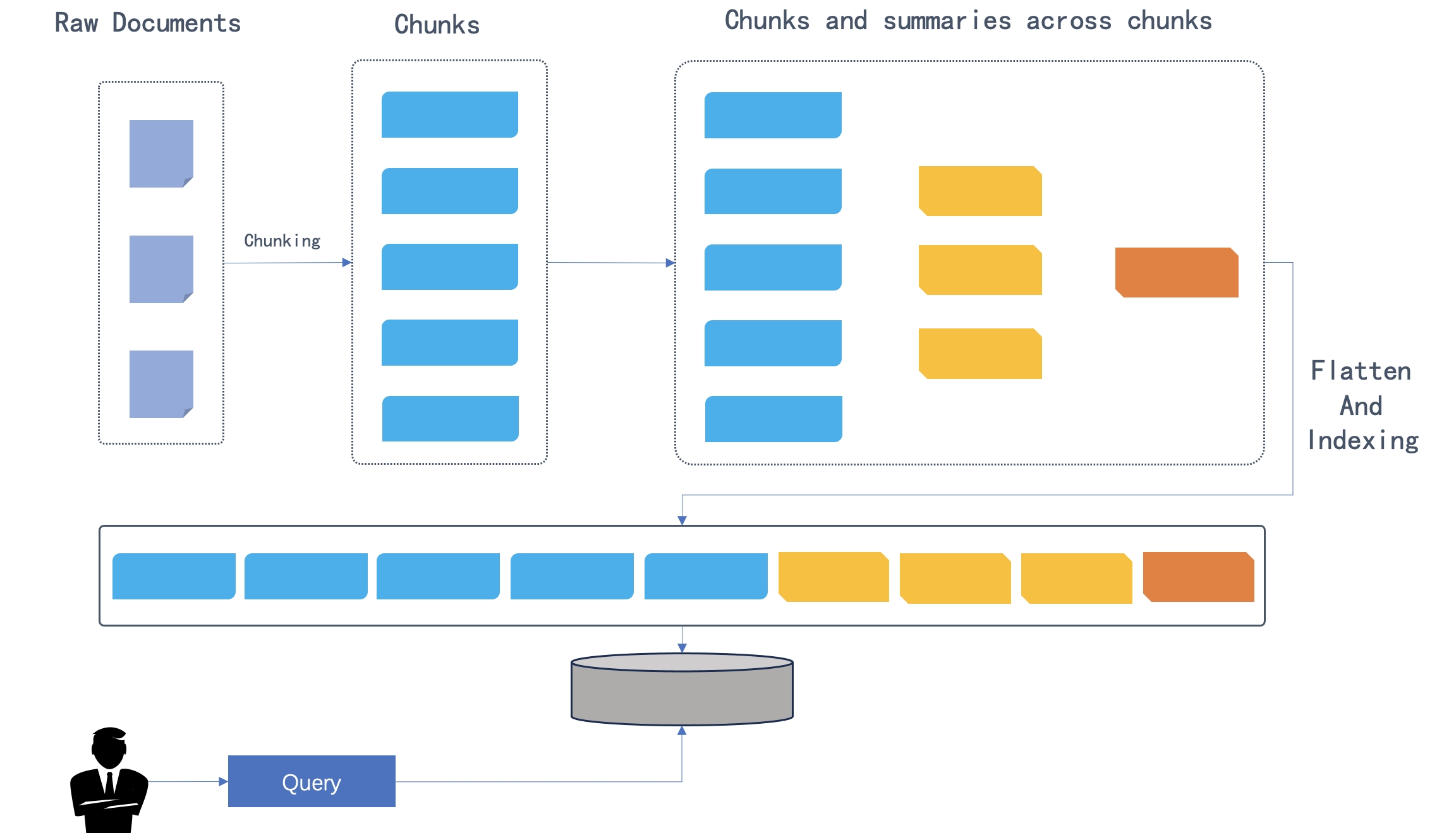
After the original documents are divided into chunks, the chunks are clustered by semantic similarity rather than by their original order in the text. Clusters are then summarized into higher-level chunks by your system's default chat model. This process is applied recursively, forming a tree structure with various levels of summarization from the bottom up. As illustrated in the figure below, the initial chunks form the leaf nodes (shown in blue) and are recursively summarized into a root node (shown in orange).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The recursive clustering and summarization capture a broad understanding (by the root node) as well as fine details (by the leaf nodes) necessary for multi-hop question-answering.
|
||||
|
||||
## Scenarios
|
||||
|
||||
For multi-hop question-answering tasks involving complex, multi-step reasoning, a semantic gap often exists between the question and its answer. As a result, searching with the question often fails to retrieve the relevant chunks that contribute to the correct answer. RAPTOR addresses this challenge by providing the chat model with richer and more context-aware and relevant chunks to summarize, enabling a holistic understanding without losing granular details.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip NOTE
|
||||
Knowledge graphs can also be used for multi-hop question-answering tasks. See [Construct knowledge graph](./construct_knowledge_graph.md) for details. You may use either approach or both, but ensure you understand the memory, computational, and token costs involved.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
The system's default chat model is used to summarize clustered content. Before proceeding, ensure that you have a chat model properly configured:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Configurations
|
||||
|
||||
The RAPTOR feature is disabled by default. To enable it, manually switch on the **Use RAPTOR to enhance retrieval** toggle on your dataset's **Configuration** page.
|
||||
|
||||
### Prompt
|
||||
|
||||
The following prompt will be applied *recursively* for cluster summarization, with `{cluster_content}` serving as an internal parameter. We recommend that you keep it as-is for now. The design will be updated in due course.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Please summarize the following paragraphs... Paragraphs as following:
|
||||
{cluster_content}
|
||||
The above is the content you need to summarize.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Max token
|
||||
|
||||
The maximum number of tokens per generated summary chunk. Defaults to 256, with a maximum limit of 2048.
|
||||
|
||||
### Threshold
|
||||
|
||||
In RAPTOR, chunks are clustered by their semantic similarity. The **Threshold** parameter sets the minimum similarity required for chunks to be grouped together.
|
||||
|
||||
It defaults to 0.1, with a maximum limit of 1. A higher **Threshold** means fewer chunks in each cluster, while a lower one means more.
|
||||
|
||||
### Max cluster
|
||||
|
||||
The maximum number of clusters to create. Defaults to 64, with a maximum limit of 1024.
|
||||
|
||||
### Random seed
|
||||
|
||||
A random seed. Click **+** to change the seed value.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to the **Configuration** page of your dataset and update:
|
||||
|
||||
- Prompt: *Optional* - We recommend that you keep it as-is until you understand the mechanism behind.
|
||||
- Max token: *Optional*
|
||||
- Threshold: *Optional*
|
||||
- Max cluster: *Optional*
|
||||
|
||||
2. Navigate to the **Files** page of your dataset, click the **Generate** button on the top right corner of the page, then select **RAPTOR** from the dropdown to initiate the RAPTOR build process.
|
||||
|
||||
*You can click the pause button in the dropdown to halt the build process when necessary.*
|
||||
|
||||
3. Go back to the **Configuration** page:
|
||||
|
||||
*The **RAPTOR** field changes from `Not generated` to `Generated at a specific timestamp` when a RAPTOR hierarchical tree structure is generated. You can delete it by clicking the recycle bin button to the right of the field.*
|
||||
|
||||
4. Once a RAPTOR hierarchical tree structure is generated, your chat assistant and **Retrieval** agent component will use it for retrieval as a default.
|
||||
39
docs/guides/dataset/extract_table_of_contents.md
Normal file
39
docs/guides/dataset/extract_table_of_contents.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: 4
|
||||
slug: /enable_table_of_contents
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Extract table of contents
|
||||
|
||||
Extract table of contents (TOC) from documents to provide long context RAG and improve retrieval.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
During indexing, this technique uses LLM to extract and generate chapter information, which is added to each chunk to provide sufficient global context. At the retrieval stage, it first uses the chunks matched by search, then supplements missing chunks based on the table of contents structure. This addresses issues caused by chunk fragmentation and insufficient context, improving answer quality.
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger WARNING
|
||||
Enabling TOC extraction requires significant memory, computational resources, and tokens.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
The system's default chat model is used to summarize clustered content. Before proceeding, ensure that you have a chat model properly configured:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to the **Configuration** page.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Enable **TOC Enhance**.
|
||||
|
||||
3. To use this technique during retrieval, do either of the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- In the **Chat setting** panel of your chat app, switch on the **TOC Enhance** toggle.
|
||||
- If you are using an agent, click the **Retrieval** agent component to specify the dataset(s) and switch on the **TOC Enhance** toggle.
|
||||
|
||||
## Frequently asked questions
|
||||
|
||||
### Will previously parsed files be searched using the TOC enhancement feature once I enable `TOC Enhance`?
|
||||
|
||||
No. Only files parsed after you enable **TOC Enhance** will be searched using the TOC enhancement feature. To apply this feature to files parsed before enabling **TOC Enhance**, you must reparse them.
|
||||
95
docs/guides/dataset/run_retrieval_test.md
Normal file
95
docs/guides/dataset/run_retrieval_test.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: 10
|
||||
slug: /run_retrieval_test
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Run retrieval test
|
||||
|
||||
Conduct a retrieval test on your dataset to check whether the intended chunks can be retrieved.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
After your files are uploaded and parsed, it is recommended that you run a retrieval test before proceeding with the chat assistant configuration. Running a retrieval test is *not* an unnecessary or superfluous step at all! Just like fine-tuning a precision instrument, RAGFlow requires careful tuning to deliver optimal question answering performance. Your dataset settings, chat assistant configurations, and the specified large and small models can all significantly impact the final results. Running a retrieval test verifies whether the intended chunks can be recovered, allowing you to quickly identify areas for improvement or pinpoint any issue that needs addressing. For instance, when debugging your question answering system, if you know that the correct chunks can be retrieved, you can focus your efforts elsewhere. For example, in issue [#5627](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/issues/5627), the problem was found to be due to the LLM's limitations.
|
||||
|
||||
During a retrieval test, chunks created from your specified chunking method are retrieved using a hybrid search. This search combines weighted keyword similarity with either weighted vector cosine similarity or a weighted reranking score, depending on your settings:
|
||||
|
||||
- If no rerank model is selected, weighted keyword similarity will be combined with weighted vector cosine similarity.
|
||||
- If a rerank model is selected, weighted keyword similarity will be combined with weighted vector reranking score.
|
||||
|
||||
In contrast, chunks created from [knowledge graph construction](./construct_knowledge_graph.md) are retrieved solely using vector cosine similarity.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
- Your files are uploaded and successfully parsed before running a retrieval test.
|
||||
- A knowledge graph must be successfully built before enabling **Use knowledge graph**.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configurations
|
||||
|
||||
### Similarity threshold
|
||||
|
||||
This sets the bar for retrieving chunks: chunks with similarities below the threshold will be filtered out. By default, the threshold is set to 0.2. This means that only chunks with hybrid similarity score of 20 or higher will be retrieved.
|
||||
|
||||
### Vector similarity weight
|
||||
|
||||
This sets the weight of vector similarity in the composite similarity score, whether used with vector cosine similarity or a reranking score. By default, it is set to 0.3, making the weight of the other component 0.7 (1 - 0.3).
|
||||
|
||||
### Rerank model
|
||||
|
||||
- If left empty, RAGFlow will use a combination of weighted keyword similarity and weighted vector cosine similarity.
|
||||
- If a rerank model is selected, weighted keyword similarity will be combined with weighted vector reranking score.
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger IMPORTANT
|
||||
Using a rerank model will significantly increase the time to receive a response.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Use knowledge graph
|
||||
|
||||
In a knowledge graph, an entity description, a relationship description, or a community report each exists as an independent chunk. This switch indicates whether to add these chunks to the retrieval.
|
||||
|
||||
The switch is disabled by default. When enabled, RAGFlow performs the following during a retrieval test:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Extract entities and entity types from your query using the LLM.
|
||||
2. Retrieve top N entities from the graph based on their PageRank values, using the extracted entity types.
|
||||
3. Find similar entities and their N-hop relationships from the graph using the embeddings of the extracted query entities.
|
||||
4. Retrieve similar relationships from the graph using the query embedding.
|
||||
5. Rank these retrieved entities and relationships by multiplying each one's PageRank value with its similarity score to the query, returning the top n as the final retrieval.
|
||||
6. Retrieve the report for the community involving the most entities in the final retrieval.
|
||||
*The retrieved entity descriptions, relationship descriptions, and the top 1 community report are sent to the LLM for content generation.*
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger IMPORTANT
|
||||
Using a knowledge graph in a retrieval test will significantly increase the time to receive a response.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Cross-language search
|
||||
|
||||
To perform a [cross-language search](../../references/glossary.mdx#cross-language-search), select one or more target languages from the dropdown menu. The system’s default chat model will then translate your query entered in the Test text field into the selected target language(s). This translation ensures accurate semantic matching across languages, allowing you to retrieve relevant results regardless of language differences.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip NOTE
|
||||
- When selecting target languages, please ensure that these languages are present in the dataset to guarantee an effective search.
|
||||
- If no target language is selected, the system will search only in the language of your query, which may cause relevant information in other languages to be missed.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Test text
|
||||
|
||||
This field is where you put in your testing query.
|
||||
|
||||
## Procedure
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to the **Retrieval testing** page of your dataset, enter your query in **Test text**, and click **Testing** to run the test.
|
||||
2. If the results are unsatisfactory, tune the options listed in the Configuration section and rerun the test.
|
||||
|
||||
*The following is a screenshot of a retrieval test conducted without using knowledge graph. It demonstrates a hybrid search combining weighted keyword similarity and weighted vector cosine similarity. The overall hybrid similarity score is 28.56, calculated as 25.17 (term similarity score) x 0.7 + 36.49 (vector similarity score) x 0.3:*
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*The following is a screenshot of a retrieval test conducted using a knowledge graph. It shows that only vector similarity is used for knowledge graph-generated chunks:*
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
:::caution WARNING
|
||||
If you have adjusted the default settings, such as keyword similarity weight or similarity threshold, to achieve the optimal results, be aware that these changes will not be automatically saved. You must apply them to your chat assistant settings or the **Retrieval** agent component settings.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Frequently asked questions
|
||||
|
||||
### Is an LLM used when the Use Knowledge Graph switch is enabled?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, your LLM will be involved to analyze your query and extract the related entities and relationship from the knowledge graph. This also explains why additional tokens and time will be consumed.
|
||||
76
docs/guides/dataset/select_pdf_parser.md
Normal file
76
docs/guides/dataset/select_pdf_parser.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: -4
|
||||
slug: /select_pdf_parser
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Select PDF parser
|
||||
|
||||
Select a visual model for parsing your PDFs.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
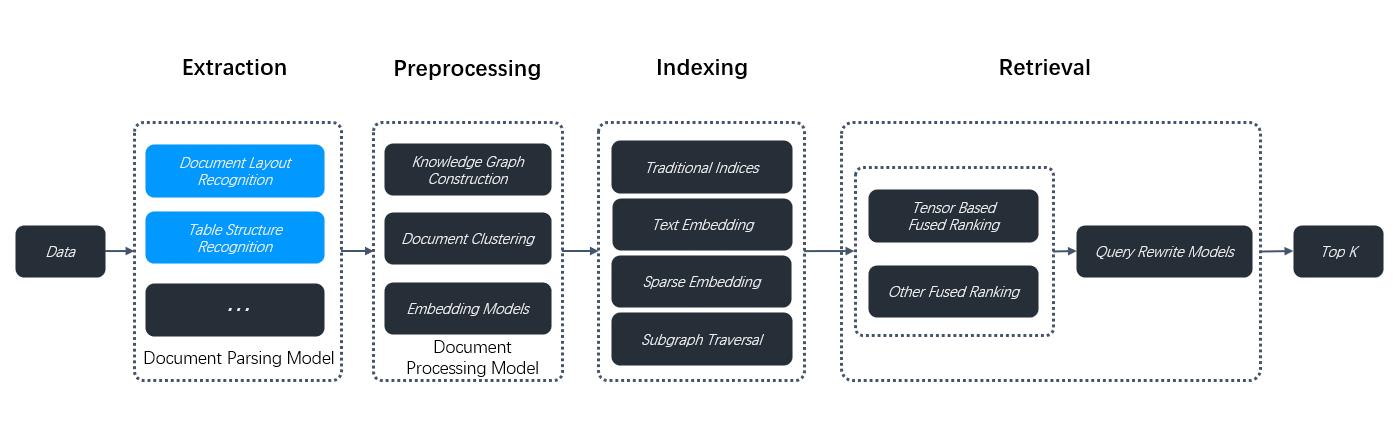
RAGFlow isn't one-size-fits-all. It is built for flexibility and supports deeper customization to accommodate more complex use cases. From v0.17.0 onwards, RAGFlow decouples DeepDoc-specific data extraction tasks from chunking methods **for PDF files**. This separation enables you to autonomously select a visual model for OCR (Optical Character Recognition), TSR (Table Structure Recognition), and DLR (Document Layout Recognition) tasks that balances speed and performance to suit your specific use cases. If your PDFs contain only plain text, you can opt to skip these tasks by selecting the **Naive** option, to reduce the overall parsing time.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
- The PDF parser dropdown menu appears only when you select a chunking method compatible with PDFs, including:
|
||||
- **General**
|
||||
- **Manual**
|
||||
- **Paper**
|
||||
- **Book**
|
||||
- **Laws**
|
||||
- **Presentation**
|
||||
- **One**
|
||||
- To use a third-party visual model for parsing PDFs, ensure you have set a default img2txt model under **Set default models** on the **Model providers** page.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
1. On your dataset's **Configuration** page, select a chunking method, say **General**.
|
||||
|
||||
_The **PDF parser** dropdown menu appears._
|
||||
|
||||
2. Select the option that works best with your scenario:
|
||||
|
||||
- DeepDoc: (Default) The default visual model performing OCR, TSR, and DLR tasks on PDFs, which can be time-consuming.
|
||||
- Naive: Skip OCR, TSR, and DLR tasks if *all* your PDFs are plain text.
|
||||
- MinerU: An experimental feature.
|
||||
- A third-party visual model provided by a specific model provider.
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger IMPORTANG
|
||||
MinerU PDF document parsing is available starting from v0.21.1. To use this feature, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Before deploying ragflow-server, update your **docker/.env** file:
|
||||
- Enable `HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.com`
|
||||
- Add a MinerU entry: `MINERU_EXECUTABLE=/ragflow/uv_tools/.venv/bin/mineru`
|
||||
|
||||
2. Start the ragflow-server and run the following commands inside the container:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
mkdir uv_tools
|
||||
cd uv_tools
|
||||
uv venv .venv
|
||||
source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
uv pip install -U "mineru[core]" -i https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Restart the ragflow-server.
|
||||
4. In the web UI, navigate to the **Configuration** page of your dataset. Click **Built-in** in the **Ingestion pipeline** section, select a chunking method from the **Built-in** dropdown, which supports PDF parsing, and slect **MinerU** in **PDF parser**.
|
||||
5. If you use a custom ingestion pipeline instead, you must also complete the first three steps before selecting **MinerU** in the **Parsing method** section of the **Parser** component.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::caution WARNING
|
||||
Third-party visual models are marked **Experimental**, because we have not fully tested these models for the aforementioned data extraction tasks.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Frequently asked questions
|
||||
|
||||
### When should I select DeepDoc or a third-party visual model as the PDF parser?
|
||||
|
||||
Use a visual model to extract data if your PDFs contain formatted or image-based text rather than plain text. DeepDoc is the default visual model but can be time-consuming. You can also choose a lightweight or high-performance img2txt model depending on your needs and hardware capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I select a visual model to parse my DOCX files?
|
||||
|
||||
No, you cannot. This dropdown menu is for PDFs only. To use this feature, convert your DOCX files to PDF first.
|
||||
|
||||
32
docs/guides/dataset/set_metadata.md
Normal file
32
docs/guides/dataset/set_metadata.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: -7
|
||||
slug: /set_metada
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Set metadata
|
||||
|
||||
Add metadata to an uploaded file
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
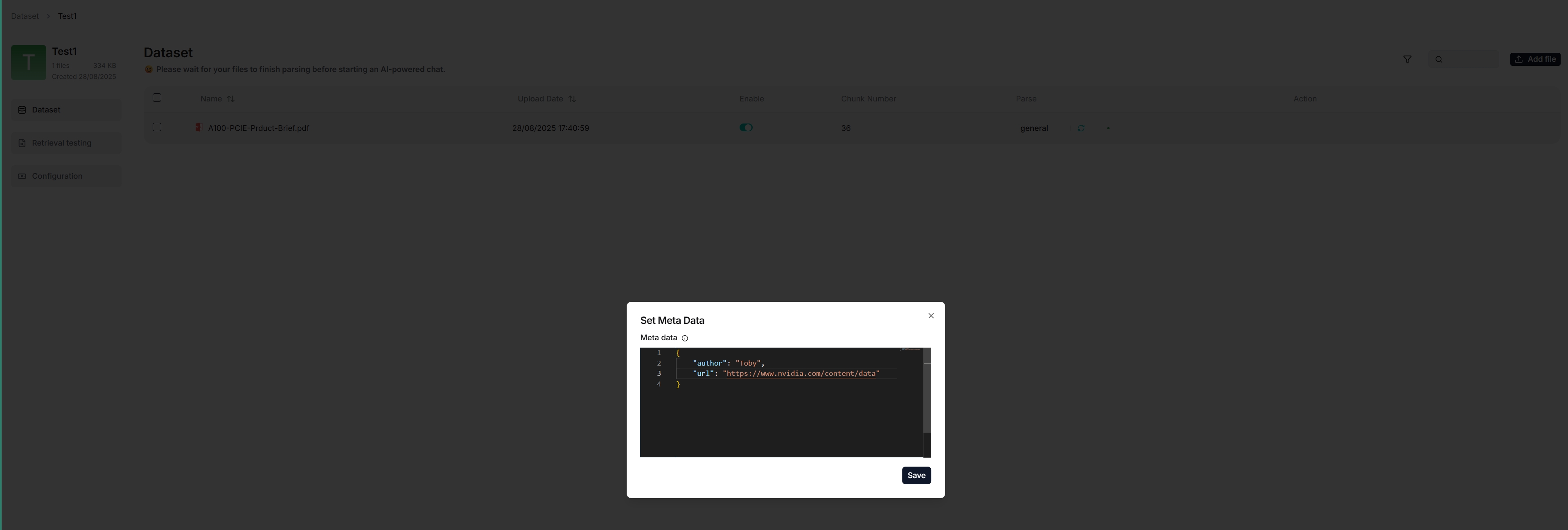
On the **Dataset** page of your dataset, you can add metadata to any uploaded file. This approach enables you to 'tag' additional information like URL, author, date, and more to an existing file. In an AI-powered chat, such information will be sent to the LLM with the retrieved chunks for content generation.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you have a dataset of HTML files and want the LLM to cite the source URL when responding to your query, add a `"url"` parameter to each file's metadata.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip NOTE
|
||||
Ensure that your metadata is in JSON format; otherwise, your updates will not be applied.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Related APIs
|
||||
|
||||
[Retrieve chunks](../../references/http_api_reference.md#retrieve-chunks)
|
||||
|
||||
## Frequently asked questions
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I set metadata for multiple documents at once?
|
||||
|
||||
No, you must set metadata *individually* for each document, as RAGFlow does not support batch setting of metadata. If you still consider this feature essential, please [raise an issue](https://github.com/infiniflow/ragflow/issues) explaining your use case and its importance.
|
||||
39
docs/guides/dataset/set_page_rank.md
Normal file
39
docs/guides/dataset/set_page_rank.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: -2
|
||||
slug: /set_page_rank
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Set page rank
|
||||
|
||||
Create a step-retrieval strategy using page rank.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Scenario
|
||||
|
||||
In an AI-powered chat, you can configure a chat assistant or an agent to respond using knowledge retrieved from multiple specified datasets (datasets), provided that they employ the same embedding model. In situations where you prefer information from certain dataset(s) to take precedence or to be retrieved first, you can use RAGFlow's page rank feature to increase the ranking of chunks from these datasets. For example, if you have configured a chat assistant to draw from two datasets, dataset A for 2024 news and dataset B for 2023 news, but wish to prioritize news from year 2024, this feature is particularly useful.
|
||||
|
||||
:::info NOTE
|
||||
It is important to note that this 'page rank' feature operates at the level of the entire dataset rather than on individual files or documents.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
On the **Configuration** page of your dataset, drag the slider under **Page rank** to set the page rank value for your dataset. You are also allowed to input the intended page rank value in the field next to the slider.
|
||||
|
||||
:::info NOTE
|
||||
The page rank value must be an integer. Range: [0,100]
|
||||
|
||||
- 0: Disabled (Default)
|
||||
- A specific value: enabled
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip NOTE
|
||||
If you set the page rank value to a non-integer, say 1.7, it will be rounded down to the nearest integer, which in this case is 1.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Scoring mechanism
|
||||
|
||||
If you configure a chat assistant's **similarity threshold** to 0.2, only chunks with a hybrid score greater than 0.2 x 100 = 20 will be retrieved and sent to the chat model for content generation. This initial filtering step is crucial for narrowing down relevant information.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have assigned a page rank of 1 to dataset A (2024 news) and 0 to dataset B (2023 news), the final hybrid scores of the retrieved chunks will be adjusted accordingly. A chunk retrieved from dataset A with an initial score of 50 will receive a boost of 1 x 100 = 100 points, resulting in a final score of 50 + 1 x 100 = 150. In this way, chunks retrieved from dataset A will always precede chunks from dataset B.
|
||||
103
docs/guides/dataset/use_tag_sets.md
Normal file
103
docs/guides/dataset/use_tag_sets.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
sidebar_position: 6
|
||||
slug: /use_tag_sets
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
# Use tag set
|
||||
|
||||
Use a tag set to auto-tag chunks in your datasets.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Retrieval accuracy is the touchstone for a production-ready RAG framework. In addition to retrieval-enhancing approaches like auto-keyword, auto-question, and knowledge graph, RAGFlow introduces an auto-tagging feature to address semantic gaps. The auto-tagging feature automatically maps tags in the user-defined tag sets to relevant chunks within your dataset based on similarity with each chunk. This automation mechanism allows you to apply an additional "layer" of domain-specific knowledge to existing datasets, which is particularly useful when dealing with a large number of chunks.
|
||||
|
||||
To use this feature, ensure you have at least one properly configured tag set, specify the tag set(s) on the **Configuration** page of your dataset, and then re-parse your documents to initiate the auto-tagging process. During this process, each chunk in your dataset is compared with every entry in the specified tag set(s), and tags are automatically applied based on similarity.
|
||||
|
||||
## Scenarios
|
||||
|
||||
Auto-tagging applies in situations where chunks are so similar to each other that the intended chunks cannot be distinguished from the rest. For example, when you have a few chunks about iPhone and a majority about iPhone case or iPhone accessaries, it becomes difficult to retrieve those chunks about iPhone without additional information.
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. Create tag set
|
||||
|
||||
You can consider a tag set as a closed set, and the tags to attach to the chunks in your dataset are *exclusively* from the specified tag set. You use a tag set to "inform" RAGFlow which chunks to tag and which tags to apply.
|
||||
|
||||
### Prepare a tag table file
|
||||
|
||||
A tag set can comprise one or multiple table files in XLSX, CSV, or TXT formats. Each table file in the tag set contains two columns, **Description** and **Tag**:
|
||||
|
||||
- The first column provides descriptions of the tags listed in the second column. These descriptions can be example chunks or example queries. Similarity will be calculated between each entry in this column and every chunk in your dataset.
|
||||
- The **Tag** column includes tags to pair with the description entries. Multiple tags should be separated by a comma (,).
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip NOTE
|
||||
As a rule of thumb, consider including the following entries in your tag table:
|
||||
|
||||
- Descriptions of intended chunks, along with their corresponding tags.
|
||||
- User queries that fail to retrieve the correct responses using other methods, ensuring their tags match the intended chunks in your dataset.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a tag set
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger IMPORTANT
|
||||
A tag set is *not* involved in document indexing or retrieval. Do not specify a tag set when configuring your chat assistant or agent.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click **+ Create dataset** to create a dataset.
|
||||
2. Navigate to the **Configuration** page of the created dataset, select **Built-in** in **Ingestion pipeline**, then choose **Tag** as the default chunking method from the **Built-in** drop-down menu.
|
||||
3. Go back to the **Files** page and upload and parse your table file in XLSX, CSV, or TXT formats.
|
||||
_A tag cloud appears under the **Tag view** section, indicating the tag set is created:_
|
||||

|
||||
4. Click the **Table** tab to view the tag frequency table:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 2. Tag chunks
|
||||
|
||||
Once a tag set is created, you can apply it to your dataset:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to the **Configuration** page of your dataset.
|
||||
2. Select the tag set from the **Tag sets** dropdown and click **Save** to confirm.
|
||||
|
||||
:::tip NOTE
|
||||
If the tag set is missing from the dropdown, check that it has been created or configured correctly.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
3. Re-parse your documents to start the auto-tagging process.
|
||||
_In an AI chat scenario using auto-tagged datasets, each query will be tagged using the corresponding tag set(s) and chunks with these tags will have a higher chance to be retrieved._
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. Update tag set
|
||||
|
||||
Creating a tag set is *not* for once and for all. Oftentimes, you may find it necessary to update or delete existing tags or add new entries.
|
||||
|
||||
- You can update the existing tag set in the tag frequency table.
|
||||
- To add new entries, you can add and parse new table files in XLSX, CSV, or TXT formats.
|
||||
|
||||
### Update tag set in tag frequency table
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to the **Configuration** page in your tag set.
|
||||
2. Click the **Table** tab under **Tag view** to view the tag frequncy table, where you can update tag names or delete tags.
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger IMPORTANT
|
||||
When a tag set is updated, you must re-parse the documents in your dataset so that their tags can be updated accordingly.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
### Add new table files
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to the **Configuration** page in your tag set.
|
||||
2. Navigate to the **Dataset** page and upload and parse your table file in XLSX, CSV, or TXT formats.
|
||||
|
||||
:::danger IMPORTANT
|
||||
If you add new table files to your tag set, it is at your own discretion whether to re-parse your documents in your datasets.
|
||||
:::
|
||||
|
||||
## Frequently asked questions
|
||||
|
||||
### Can I reference more than one tag set?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can. Usually one tag set suffices. When using multiple tag sets, ensure they are independent of each other; otherwise, consider merging your tag sets.
|
||||
|
||||
### Difference between a tag set and a standard dataset?
|
||||
|
||||
A standard dataset is a dataset. It will be searched by RAGFlow's document engine and the retrieved chunks will be fed to the LLM. In contrast, a tag set is used solely to attach tags to chunks within your dataset. It does not directly participate in the retrieval process, and you should not choose a tag set when selecting datasets for your chat assistant or agent.
|
||||
|
||||
### Difference between auto-tag and auto-keyword?
|
||||
|
||||
Both features enhance retrieval in RAGFlow. The auto-keyword feature relies on the LLM and consumes a significant number of tokens, whereas the auto-tag feature is based on vector similarity and predefined tag set(s). You can view the keywords applied in the auto-keyword feature as an open set, as they are generated by the LLM. In contrast, a tag set can be considered a user-defined close set, requiring upload tag set(s) in specified formats before use.
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user